Energy Policy WA is developing improved protections for customers in embedded electricity networks.
Traditional supply of electricity
Most people buy electricity from a licensed retailer like Synergy or Horizon Power. They receive their electricity from the main grid. Customers have an individual meter at their property, owned and maintained by the grid operator.
Licensed retailers must provide protections to their customers. These include a mandatory Code of Conduct and access to the Energy and Water Ombudsman to resolve disputes. Licensed retailers are monitored for compliance by the Economic Regulation Authority.
What is an embedded network?
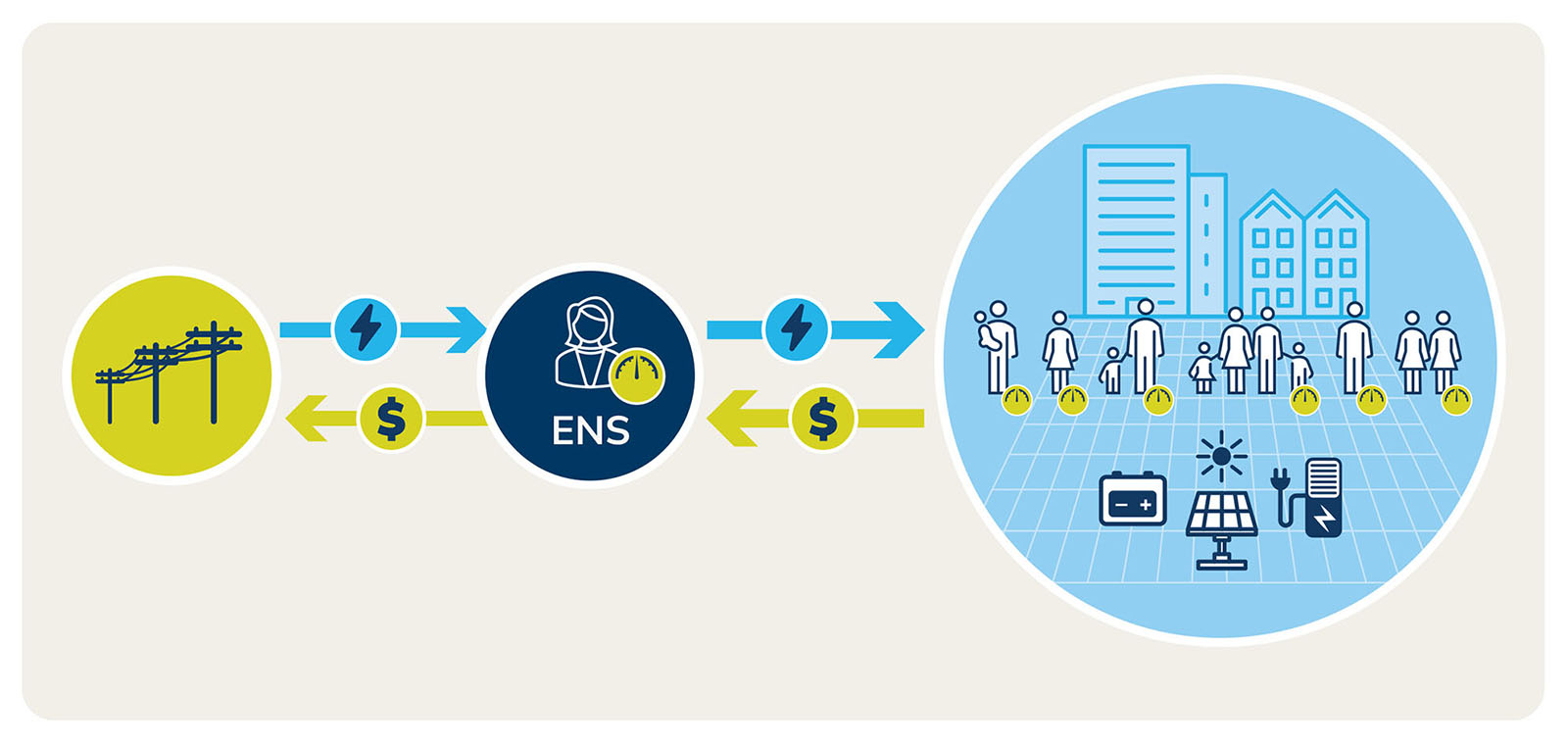
An embedded network is a private electricity network servicing several lots or tenancies in one property. The master meter connects the property to the grid. It also measures the electricity supplied for everyone on that property at that connection point.
The operator of the embedded network may be the property owner (or owners), or a third party under contract.
On-selling electricity in an embedded network
The embedded network operator buys electricity from a licensed retailer to supply the whole property. Then they on-sell that electricity to individual consumers on the property. Solar panels or batteries may contribute electricity supply for the property. The consumption of each lot or tenancy is usually measured by its own sub-meter. These sub-meters also form part of the embedded network.
Customers in an embedded network buy electricity from the embedded network operator, not from a licensed electricity retailer.
More information: On-selling of electricity and gas.
Embedded networks can take many forms
Embedded networks can be found in:
- apartment buildings
- retirement villages
- caravan and long stay parks
- shopping centres
- office blocks
- industrial parks
- university and health campuses
- airports
- seaports
A lot of (but not all) these buildings will have an embedded network. Some can have separate Western Power or Horizon Power master meters for each lot. If you receive your electricity bill from a licensed retailer such as Synergy or Horizon Power, you are not in an embedded network.
What happens if you buy electricity through an embedded network?
Embedded networks have benefits like cost savings and innovation in sustainable technologies. The main disadvantage is less customer protection than those who buy from a licensed retailer.
Limited customer protections
Electricity is an essential service. Customers of licensed retailers have certain rights protected under the Code of Conduct for the Supply of Electricity to Small Use Customers. They also have access to the Energy and Water Ombudsman to resolve disputes. The licenced retailer’s activity is monitored for compliance by the Economic Regulation Authority.
None of these protections apply if you buy electricity from an embedded network operator. Some limited customer protections apply under the licence exemption framework.
For information on the current regulations for on-selling electricity in Western Australia see our fact sheets about on-selling.
Eligible customers in embedded networks can also access concessions directly from RevenueWA through the Energy Concession Extension Scheme.